When You Know the Range and One Point
Domain and Range
Functions in mathematics can be compared to the operations of a vending (soda) motorcar. When you put in a sure corporeality of money, you tin select dissimilar types of sodas. Similarly, for functions, we input different numbers and we get new numbers every bit the result. Domain and range are the main aspects of functions. You can utilize quarters and one-dollar bills to buy a soda. The motorcar will not requite you whatever flavor of the soda if pennies are input. Hence, the domain represents the inputs we can have here, that is, quarters and i-dollar bills. No matter what corporeality you pay, y'all won't get a cheeseburger from a soda motorcar. Thus, the range is the possible outputs we tin have here, that is, the flavors of soda in the machine. Let u.s.a. learn to find the domain and range of a given role, and also graph them.
| ane. | What is Domain and Range? |
| two. | Domain and Range of a Role |
| 3. | Domain of a Function |
| 4. | Range of a Part |
| five. | How To Discover Domain And Range? |
| half-dozen. | Domain and Range of Exponential Functions |
| vii. | Domain and Range of Trigonometric Functions |
| 8. | Domain and Range of an Absolute Value Function |
| ix. | Graphs of Domain and Range |
| 10. | FAQs on Domain and Range |
What is Domain and Range?
The domain and range are divers for a relation and they are the sets of all the x-coordinates and all the y-coordinates of ordered pairs respectively. For example, if the relation is, R = {(one, 2), (2, ii), (3, 3), (4, 3)}, and then:
- Domain = the ready of all x-coordinates = {1, ii, three, 4}
- Range = the set of all y-coordinates = {2, three}
We can visualize this hither:
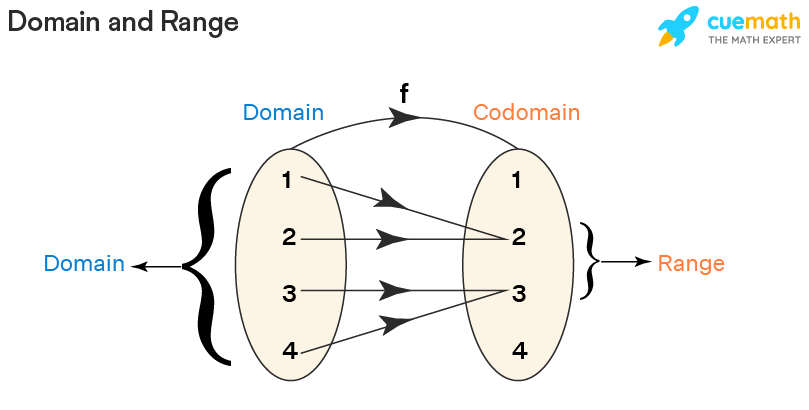
Domain and Range of a Function
The domain and range of a office are the components of a office. The domain is the set of all the input values of a function and range is the possible output given by the office. Domain→ Function →Range. If there exists a function f: A →B such that every element of A is mapped to elements in B, then A is the domain and B is the co-domain. The image of an element 'a' under a relation R is given by 'b', where (a,b) ∈ R. The range of the office is the set of images. The domain and range of a office is denoted in full general as follows: Domain(f) = {10 ∈ R} and range(f)={f(ten) : x ∈ domain(f)}
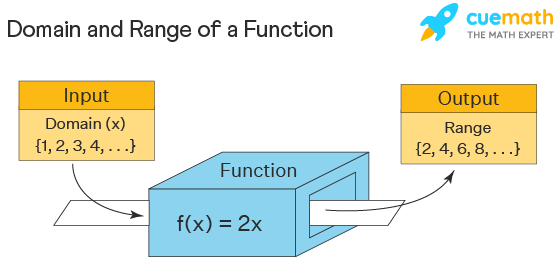
The domain and range of this function f(10) = 2x is given as domain D ={x ∈ Due north } , range R = {(y): y = 2x}
Domain of a Office
A domain of a part refers to "all the values" that get into a role. The domain of a function is the set of all possible inputs for the office. Consider this box as a role f(ten) = 2x . Inputting the values 10 = {1,2,iii,four,...}, the domain is but the set of natural numbers and the output values are called the range. Just in general, f(ten) = 2x is divers for all existent values of 10 and hence its domain is the set up of all real numbers which is denoted by (-∞, ∞). Here are the general formulas used to find the domain of different types of functions. Hither, R is the ready of all existent numbers.
- Domain of any polynomial (linear, quadratic, cubic, etc) office is R.
- Domain of a square root function √x is x≥0.
- Domain of an exponential function is R.
- Domain of logarithmic role is x>0.
- To find the domain of a rational role y = f(x), set the denominator ≠ 0.
Range of a Function
The range of a function is the prepare of all its outputs. Example: Let u.s. consider the function f: A→ B, where f(x) = 2x and each of A and B = {set of natural numbers}. Hither we say A is the domain and B is the co-domain. And then the output of this office becomes the range. The range = {set of fifty-fifty natural numbers}. The elements of the domain are called pre-images and the elements of the co-domain which are mapped are called the images. Here, the range of the function f is the set of all images of the elements of the domain (or) the set up of all the outputs of the role. In the upcoming sections, we can run into how to find the range of unlike types of functions. Hither are the general formulas used to find the range of different types of functions. Annotation that R is the set of all existent numbers here.
- Range of a linear part is R.
- Range of a quadratic function y = a(x-h)ii + k is:
y≥k, if a>0 and
y≤k, if a<0 - Range of a square root function is y≥0.
- Range of an exponential part is y>0.
- Range of logarithmic function is R.
- To find the range of a rational function y = f(x), solve it for x and set the denominator ≠ 0.
How To Find Domain And Range?
Suppose X = {ane, 2, 3, four, five}, f: X → Y, where R = {(x,y) : y = x+i}.
Domain = the input values. Thus Domain = X = {1, 2, three, 4, 5}
Range = the output values of the office = {two, 3, four, v, vi}
and the co-domain = Y = {2, iii, 4, 5, 6}
Let's understand the domain and range of some special functions taking different types of functions into consideration.
Domain and Range of Exponential Functions
The function y = ax, a ≥ 0 is defined for all real numbers. Hence, the domain of the exponential function is the unabridged real line. The exponential function ever results in a positive value. Thus, the range of the exponential function is of the form y= |ax+b| is y ∈ R , {y > 0}. Domain = R, Range = (0, ∞)
Instance: Look at the graph of this function f: 2x
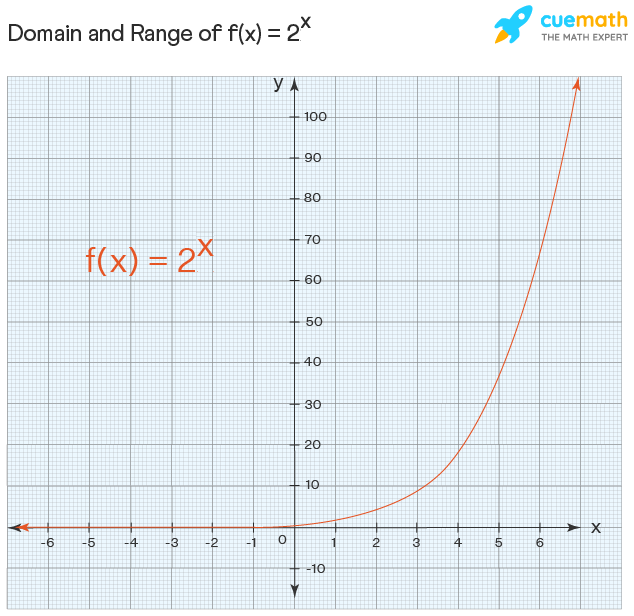
Observe that the value of the function is closer to 0 as x tends to ∞ simply information technology will never attain the value 0. The domain and range of an exponential functions are given every bit follows:
- Domain: The domain of the function is the set R.
- Range: The exponential office always results in positive real values.
Domain and Range of Trigonometric Functions
Look at the graph of the sine function and cosine office. Notice that the value of the functions oscillates between -one and 1 and it is defined for all real numbers.
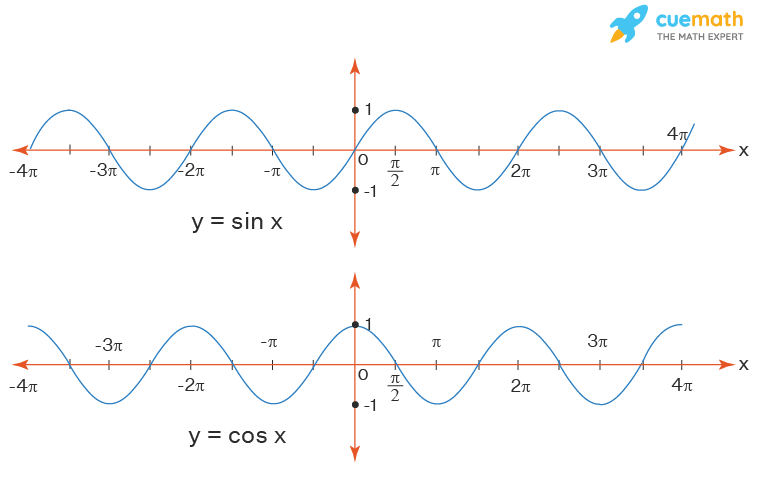
Thus, for each of the sine and cosine functions:
- Domain: The domain of the functions is the set R.
- Range: The range of the functions is [-1, 1]
The domain and range of all trigonometric functions are shown below:
| Trigonometric Functions | Domain | Range |
|---|---|---|
| Sinθ | (-∞, + ∞) | [-1, +one] |
| Cosθ | (-∞ +∞) | [-1, +1] |
| Tanθ | R - (2n + one)π/two | (-∞, +∞) |
| Cotθ | R - nπ | (-∞, +∞) |
| Secθ | R - (2n + ane)π/2 | (-∞, -1] U [+1, +∞) |
| Cosecθ | R - nπ | (-∞, -1] U [+ane, +∞) |
Domain and Range of an Accented Value Function
The function y=|ax+b| is defined for all real numbers. So, the domain of the absolute value function is the set of all existent numbers. The absolute value of a number always results in a non-negative value. Thus, the range of an absolute value function of the form y= |ax+b| is y ∈ R | y ≥ 0. The domain and range of an accented value function are given as follows
- Domain = R
- Range = [0, ∞)
Example: |6-x|
- Domain: The domain of the office is the prepare R.
- Range: We already know that the absolute value function results in a non-negative value always. i.e., |vi-x| ≥ 0, for all x.
Domain and Range of a Square Root Function
The office y= √(ax+b) is defined only for x ≥ -b/a
So, the domain of the square root function is the set of all real numbers greater than or equal to b/a. We know that the foursquare root of something ever results in a non-negative value. Thus, the range of a square root function is the set of all non-negative existent numbers. The domain and range of a square root function are given as: Domain = [-b/a,∞), Range = [0,∞)
Case: y= 2- √(-3x+2)
Domain: A square root function is defined only when the value inside it is a non-negative number. And then for a domain,
-3x+ii ≥ 0
-3x ≥ -2
10 ≤ 2/3
Range: Nosotros already know that the square root function results in a non-negative value always.
√(-3x+2)≥ 0
Multiply -ane on both sides
-√(-3x+2) ≤ 0
Calculation 2 on both sides
2-√(-3x+2)≤ 2
y≤ 2
Graphs of Domain and Range
Another manner to place the domain and range of functions is by using graphs. The domain refers to the set of possible input values. The domain of a graph consists of all the input values shown on the x-centrality. The range is the prepare of possible output values shown on the y-axis. The easiest method to notice the range of function is by graphing it and looking for the y-values covered by the graph. To find the range of a quadratic role, it is sufficient to see if information technology has a maximum or minimum value. The maximum/minimum value of a quadratic function is the y-coordinate of its vertex. To observe the domain of the rational function, set the denominator as 0 and solve for the variable. The domain is denoted by all the values from left to right along the x-axis and the range is given by the bridge of the graph from the top to the bottom.
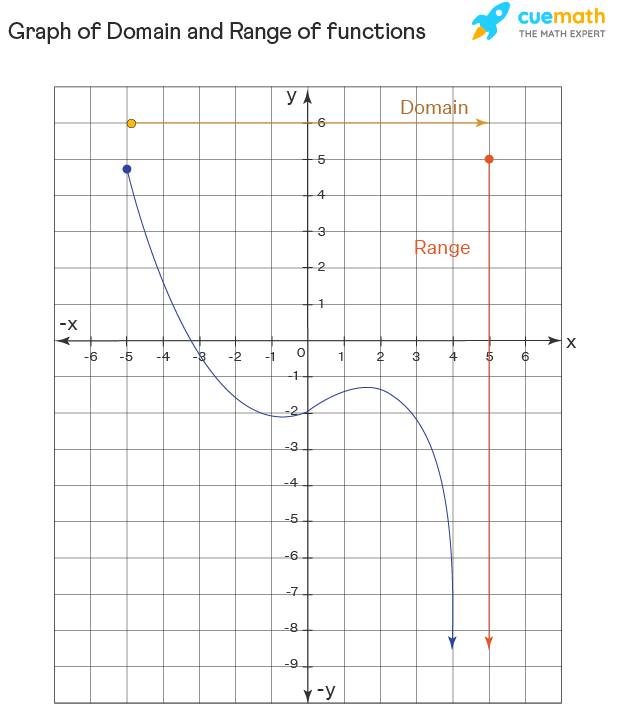
Important Notes on Domain and Range:
- The domain and range of office is the set of all possible inputs and outputs of a office respectively.
- The domain and range of a function y = f(x) is given as domain= {ten ,x∈R }, range= {f(x), x∈Domain}.
- The domain and range of any part can be establish algebraically or graphically.
☛ Also Check:
- Graphing Functions
- Cubic Functions
- Changed Trigonometric Functions
Examples on Domain and Range
go to slidego to slidego to slide

Neat learning in high school using simple cues
Indulging in rote learning, yous are likely to forget concepts. With Cuemath, you will acquire visually and be surprised by the outcomes.
Book a Free Trial Class
Exercise Questions on Domain and Range
go to slidego to slide
FAQs on Domain and Range
What is the Domain and Range of a Function?
The domain and range of a role are the ready of all the inputs and outputs a function can give respectively. The domain and range are important aspects of a function. The domain takes all the possible input values from the set of real numbers and the range takes all the output values of the office.
How Practice You Write the Domain and Range?
We write the domain and range of a function equally the set of all the inputs a function can take and the outputs of the functions respectively. The domain and range are written from the smaller values to the larger values. The domain is written from left to right and the range is written from the tiptop of the graph to the bottom.
What is The Natural Domain and Range of a Part?
The natural domain and range of a role are all the possible input values and the output values of the function respectively. Domain(f) = {10∈R} and range(f)={f(x):x ∈ domain(f)}.
What is The Domain and Range of a Constant Function?
Permit the constant function be f(x)=one thousand. The domain of a constant role is given by R, that is, the set up of real numbers. The range of a constant function is given by the singleton set, {grand}. The domain and range of a abiding function is given equally domain = x∈R and range = {k}, which is a singleton prepare.
How to Find the Domain of a Function which is Rational?
To find the domain of a rational role, nosotros just set the denominator not equal to nil. For example, to find the domain of f(x) = 2/(x-3), we set x-3 ≠ 0, by solving this, we get x≠3. So the domain is the set of all rational numbers except iii. This can be written in the interval notation as (-∞, 3) U (3, ∞).
How to Find the Range of a Rational Role?
To find the range of a rational role, nosotros but solve the equation for x and utilize set the denominator not equal to naught. For instance, to find the range of y=2/(x-3), solve it for ten first. Then nosotros get, x-iii = two/y and from this, x = (ii/y) + 3. Then its range is y≠0 (or) in interval note, (-∞, 0) U (0, ∞).
What are the Rules to Detect the Domain of a Function?
Here are some general rules used to find domain of dissimilar types of functions:
- f(x) = polynomial, the domain is the prepare of all existent numbers.
- f(x) = ane/x, domain if the set of all real numbers but x≠0.
- f(x) = √x, domain if the set of all real numbers such that 10 ≥ 0.
- f(x) = ln 10, domain is the set of all existent numbers such that 10 > 0.
How to Find The Domain and Range of Role Algebraically?
Permit the part be y=f(x). Let united states find the domain and range of this part algebraically.
To summate the domain of the office, we only solve the equation to determine the values of the contained variable 10. To calculate the range of the function, we simply express ten as x = g(y) and then find the domain of thou(y).
How to Find The Domain and Range of an Equation?
To notice the domain and range, we simply solve the equation y = f(x) to determine the values of the independent variable x and obtain the domain. To calculate the range of the office, nosotros simply limited x as x=g(y) and then find the domain of thousand(y).
What Is The Difference Between Domain and Range of a Function?
Domain and Range of a function are the components of a function. The domain of a part is the set of all possible inputs for the function, whereas the range of role is the fix of all the outputs a part tin can requite.
What is The Domain and Range of a Relation?
the domain and range of a relation is constitute as follows. Let R be the relation from a non-empty gear up A to a non-empty ready B. The domain and range of the relation are the set of showtime elements and the 2d elements respectively in the ordered pairs in relation R is called the domain.
What is the Domain and Range of Blended Functions?
Let the composite function be \(h=f \circ g\). The domain and range of h are determined every bit follows. The domain of h is either same equally f or lies within the domain of f. The range h must lie within the range of g. Let f(x) = x2 and g(ten) = x+ 3. We know that f: Ten →Y and g: Y →Z. Then fog: 10 →Z. f(g(x)) = (x+3)2. Thus the domain and range are: domain= {All the elements in set X}, range= {all the elements in set Z}
What is the Domain and Range of a Quadratic Function?
The domain and range of a quadratic function y=a(x-h)ii+thousand determine the nature of the parabola: whether it is upwards or downward or facing to the left or to the right.
- y ≥ one thousand, if the function has a minimum value, that is, when a>0(parabola opens up)
- y ≤ k, if the function has a maximum value, that is, when a<0(parabola opens down)
Source: https://www.cuemath.com/calculus/domain-and-range-of-a-function/
0 Response to "When You Know the Range and One Point"
Postar um comentário